Quelle:
RATTE, Seite 264 (Angabe genauer Cent-Zahlen) T 122
Elias Nikolaus Ammerbach, 1571,
1583 (Interpretation 2)
Verteilung
des pK ≡ 23.46 cent Verteilung des pK im Quintenzirkel
(*
Näherungswerte)
f
------ c 3/2 . 3/2
b -
3.000 f . .
es -
6.000 b - 1/8 pK*
c - 1/4 pK*
gis +
17.540 es f
│ g
cis - 4.000 gis .
│
.
fis - 6.000 cis b
│
d
h - 4.000
fis - 1/4 pK* │ - 1/4 pK*
e - 2.000
h . es───────┼────────a
.
a - 4.000
e
│
d - 6.000
a + 3/4 pK* gis
│ e - 1/6
pK*
g - 6.000
d . │ .
c ------
g
cis │ h
================== - 1/6 pK*
fis - 1/24 pK*
- 23.460 . .
.
- 1/4
pK* - 1/6 pK*
|
|
Quinten |
|
Quarten |
|
Großterzen |
|
Kleinterzen |
|
|||||
|
f |
701.955 |
c |
498.045 |
f |
395.820 |
a |
306.135 |
c |
|||||
|
b |
698.955 |
f |
501.045 |
b |
398.820 |
d |
300.135 |
f |
|||||
|
es |
695.955 |
b |
504.045 |
es |
398.820 |
g |
297.135 |
b |
|||||
|
gis |
719.495 |
es |
480.505 |
gis |
416.360 |
c |
303.135 |
es |
|||||
|
cis |
697.955 |
gis |
502.045 |
cis |
412.360 |
f |
285.595 |
gis |
|||||
|
fis |
695.955 |
cis |
504.045 |
fis |
409.360 |
b |
286.595 |
cis |
|||||
|
h |
697.955 |
fis |
502.045 |
h |
411.360 |
es |
286.595 |
fis |
|||||
|
e |
699.955 |
h |
500.045 |
e |
391.820 |
gis |
308.135 |
h |
|||||
|
a |
697.955 |
e |
502.045 |
a |
391.820 |
cis |
306.135 |
e |
|||||
|
d |
695.955 |
a |
504.045 |
d |
391.820 |
fis |
304.135 |
a |
|||||
|
g |
695.955 |
d |
504.045 |
g |
398.820 |
h |
306.135 |
d |
|||||
|
c |
701.955 |
g |
498.045 |
c |
391.820 |
e |
310.135 |
g |
|||||
|
Intervall-bezeichnung |
Quotient |
Dezimal-zahl |
Centwert des Intervalls |
Frequenzbeispiele (Zahlen in Hz) |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Oktave |
2/1 |
2.0 |
1200.000 |
c |
525.2 |
>440.0< |
a |
||||||
|
gr.Septime |
243/128x200Ö8 |
1.8788013 |
1091.775 |
h |
493.4 |
413.3 |
gis |
||||||
|
kl.Septime |
16x400Ö2/9 |
1.7808611 |
999.090 |
b |
467.7 |
391.8 |
g |
||||||
|
gr.Sexte |
27/16x100Ö2 |
1.6758436 |
893.865 |
a |
>440.0< |
368.7 |
fis |
||||||
|
kl.Sexte |
38/212x75Ö4 |
1.5724709 |
783.640 |
gis |
412.9 |
345.9 |
f |
||||||
|
Quinte |
3/2 |
1.5 |
701.955 |
g |
393.9 |
330.0 |
e |
||||||
|
Tritonus |
729/512x600Ö211 |
1.4058490 |
589.730 |
fis |
369.2 |
309.3 |
es |
||||||
|
Quarte |
4/3 |
1.3333333 |
498.045 |
f |
350.1 |
293.3 |
d |
||||||
|
gr.Terz |
81/64x75Ö2 |
1.2539820 |
391.820 |
e |
329.3 |
275.9 |
cis |
||||||
|
kl.Terz |
32x400Ö8/27 |
1.1913625 |
303.135 |
es |
312.9 |
262.1 |
c |
||||||
|
Ganzton |
9/8x200Ö2 |
1.1211078 |
197.910 |
d |
294.4 |
246.6 |
h |
||||||
|
Halbton |
2187/2048x300Ö27 |
1.0507389 |
85.685 |
cis |
275.9 |
231.2 |
b |
||||||
|
Grundton |
1/1 |
1.0 |
0.000 |
C |
262.6 |
220.0 |
a |
||||||
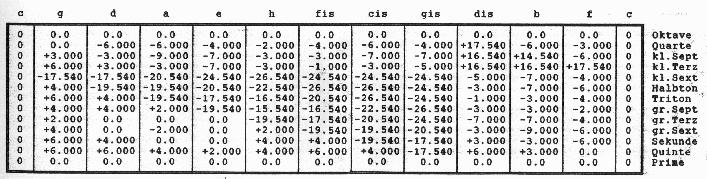
Abweichungen der
Tonstufen bei Modulationen (Zahlen in Cent)
in der Tabelle zur Graphik „Profil“: