Quelle:
RATTE, Seite 265 (Beschreibung Monochordteilung) T 123
Cyriacus Schneegass, 1590 (1. Methode:
rationale Approximation)
Verteilung
des pK ≡ 23.46 cent Verteilung des pK im Quintenzirkel
(* genähert:
321/320* ca. 1/4 pK)
f
- 5.4016 c -321/320 . -321/320
b - 5.4016
f
. .
es - 5.4016 b -321/320
c -321/320
gis
+35.9576 es f
│ g
cis - 5.4016
gis . │ .
fis - 5.4016
cis
b │ d
h - 5.4016
fis -321/320 │ -321/320
e - 5.4016
h . es───────┼────────a .
a - 5.4016
e
│
d - 5.4016
a + 3/2 pK* gis
│
e -321/320
g - 5.4016
d . │ .
c - 5.4016
g
cis │ h
================== -321/320
fis -321/320
- 23.460 . .
.
-321/320 -321/320
|
|
Quinten |
|
Quarten |
|
Großterzen |
|
Kleinterzen |
|
|||||
|
f |
696.5534 |
c |
503.4466 |
f |
386.2136 |
a |
310.3398 |
c |
|||||
|
b |
696.5534 |
f |
503.4466 |
b |
386.2136 |
d |
310.3398 |
f |
|||||
|
es |
696.5534 |
b |
503.4466 |
es |
386.2136 |
g |
310.3398 |
b |
|||||
|
gis |
737.9126 |
es |
462.0874 |
gis |
427.5728 |
c |
310.3398 |
es |
|||||
|
cis |
696.5534 |
gis |
503.4466 |
cis |
427.5728 |
f |
268.9806 |
gis |
|||||
|
fis |
696.5534 |
cis |
503.4466 |
fis |
427.5728 |
b |
268.9806 |
cis |
|||||
|
h |
696.5534 |
fis |
503.4466 |
h |
427.5728 |
es |
268.9806 |
fis |
|||||
|
e |
696.5534 |
h |
503.4466 |
e |
386.2136 |
gis |
310.3398 |
h |
|||||
|
a |
696.5534 |
e |
503.4466 |
a |
386.2136 |
cis |
310.3398 |
e |
|||||
|
d |
696.5534 |
a |
503.4466 |
d |
386.2136 |
fis |
310.3398 |
a |
|||||
|
g |
696.5534 |
d |
503.4466 |
g |
386.2136 |
h |
310.3398 |
d |
|||||
|
c |
696.5534 |
g |
503.4466 |
c |
386.2136 |
e |
310.3398 |
g |
|||||
|
Intervall-bezeichnung |
Quotient |
Dezimal-zahl |
Centwert des Intervalls |
Frequenzbeispiele (Zahlen in Hz) |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Oktave |
2/1 |
2.0 |
1200.0000 |
c |
526.4 |
>440.0< |
a |
||||||
|
gr.Septime |
1605/4x1075 |
1.8690509 |
1082.7670 |
h |
491.9 |
411.2 |
gis |
||||||
|
kl.Septime |
1072/802 |
1.7889063 |
1006.8932 |
b |
470.8 |
393.6 |
g |
||||||
|
gr.Sexte |
1603/2x1073 |
1.6717781 |
889.6602 |
a |
>440.0< |
367.8 |
fis |
||||||
|
kl.Sexte |
1608/16x1078 |
1.5623193 |
772.4272 |
gis |
411.2 |
352.0 |
f |
||||||
|
Quinte |
160/107 |
1.4953271 |
696.5534 |
g |
393.6 |
329.0 |
e |
||||||
|
Tritonus |
1606/8x1076 |
1.3974213 |
579.3204 |
fis |
367.8 |
307.4 |
es |
||||||
|
Quarte |
107/80 |
1.3375 |
503.4466 |
f |
352.0 |
295.0 |
d |
||||||
|
gr.Terz |
1604/4x1074 |
1.2499277 |
386.2136 |
e |
329.0 |
275.0 |
cis |
||||||
|
kl.Terz |
1073/2x803 |
1.1963311 |
310.3398 |
es |
314.9 |
263.2 |
c |
||||||
|
Ganzton |
1602/2x1072 |
1.1180016 |
193.1068 |
d |
294.3 |
246.0 |
h |
||||||
|
Halbton |
1607/16x1077 |
1.0448010 |
75.8738 |
cis |
275.0 |
229.9 |
b |
||||||
|
Grundton |
1/1 |
1.0 |
0.0000 |
C |
263.2 |
220.0 |
a |
||||||
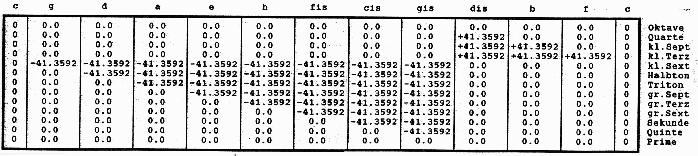
Abweichungen der
Tonstufen bei Modulationen (Zahlen in Cent)
in der Tabelle zur Graphik „Profil“: