Quelle:
RATTE, Seite 268 (Angabe genauer Cent-Zahlen) T 124
Cyriacus Schneegass, 1590 (2. Methode:
geometrische Approximation)
Verteilung
des pK ≡ 23.46 cent Verteilung des pK im Quintenzirkel
f
- 5.402 c - 321/320 . -
321/320
b - 5.402
f A = . .
es - 5.402 b 31291 - 321/320
c - 321/320
gis + 32.829(!)es 31250
f g
cis - 5.402 gis . .
fis - 5.402 cis b d
h - 5.402 fis - 321/320 - 321/320
e -
5.402 h . es
+ a .
a ! -
2.269! e B =
d - 5.402
a 7879 + B gis e
- A
g - 5.402
d 7731 . .
c - 5.402
g
cis h
================== - 321/320
fis - 321/320
- 23.460 . .
.
-
321/320 - 321/320
|
|
Quinten |
|
Quarten |
|
Großterzen |
|
Kleinterzen |
|
|||||
|
f |
696.553 |
c |
503.447 |
f |
386.212 |
a |
310.341 |
c |
|||||
|
b |
696.553 |
f |
503.447 |
b |
386.212 |
d |
310.341 |
f |
|||||
|
es |
696.553 |
b |
503.447 |
es |
386.212 |
g |
310.341 |
b |
|||||
|
gis |
734.784 |
es |
465.216 |
gis |
424.443 |
c |
310.341 |
es |
|||||
|
cis |
696.553 |
gis |
503.447 |
cis |
424.443 |
f |
272.110 |
gis |
|||||
|
fis |
696.553 |
cis |
503.447 |
fis |
424.443 |
b |
272.110 |
cis |
|||||
|
h |
696.553 |
fis |
503.447 |
h |
424.443 |
es |
272.110 |
fis |
|||||
|
e |
696.553 |
h |
503.447 |
e |
386.212 |
gis |
310.341 |
h |
|||||
|
a |
! 699.686 ! |
e |
! 500.314 ! |
a |
389.345 |
cis |
310.341 |
e |
|||||
|
d |
696.553 |
a |
503.447 |
d |
389.345 |
fis |
307.208 |
a |
|||||
|
g |
696.553 |
d |
503.447 |
g |
389.345 |
h |
307.208 |
d |
|||||
|
c |
696.553 |
g |
503.447 |
c |
389.345 |
e |
307.208 |
g |
|||||
|
Intervall-bezeichnung |
Quotient |
Dezimal-zahl |
Centwert des Intervalls |
Frequenzbeispiele (Zahlen in Hz) |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Oktave |
2/1 |
2.0 |
1200.000 |
c |
526.4 |
>440.0< |
a |
||||||
|
gr.Septime |
3x1604x56/4x1074x377x83 |
1.8724342 |
1085.898 |
h |
492.8 |
411.9 |
gis |
||||||
|
kl.Septime |
4x1072/1602 |
1.7889063 |
1006.894 |
b |
470.8 |
393.6 |
g |
||||||
|
gr.Sexte |
1603/2x1073 |
1.6717781 |
889.659 |
a |
>440.0< |
367.8 |
fis |
||||||
|
kl.Sexte |
3x1607x56/16x1077x377x83 |
1.5651463 |
775.557 |
gis |
411.9 |
344.3 |
f |
||||||
|
Quinte |
160/107 |
1.4953271 |
696.553 |
g |
393.6 |
329.0 |
e |
||||||
|
Tritonus |
3x1605x56/8x1075x377x83 |
1.3999505 |
582.451 |
fis |
368.5 |
308.0 |
es |
||||||
|
Quarte |
2x107/160 |
1.3375 |
503.447 |
f |
352.0 |
294.3 |
d |
||||||
|
gr.Terz |
3x1603x56/4x1073x377x83 |
1.2521906 |
389.345 |
e |
329.6 |
275.5 |
cis |
||||||
|
kl.Terz |
4x1073/1603 |
1.1963311 |
310.341 |
es |
314.9 |
263.2 |
c |
||||||
|
Ganzton |
1602/2x1072 |
1.1180016 |
193.106 |
d |
294.3 |
246.0 |
h |
||||||
|
Halbton |
3x1606x56/16x1076x377x83 |
1.0466918 |
79.004 |
cis |
275.5 |
230.3 |
b |
||||||
|
Grundton |
1/1 |
1.0 |
0.000 |
C |
263.2 |
220.0 |
a |
||||||
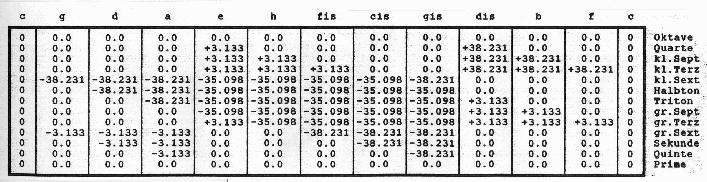
Abweichungen der
Tonstufen bei Modulationen (Zahlen in Cent)
in der Tabelle zur Graphik „Profil“: